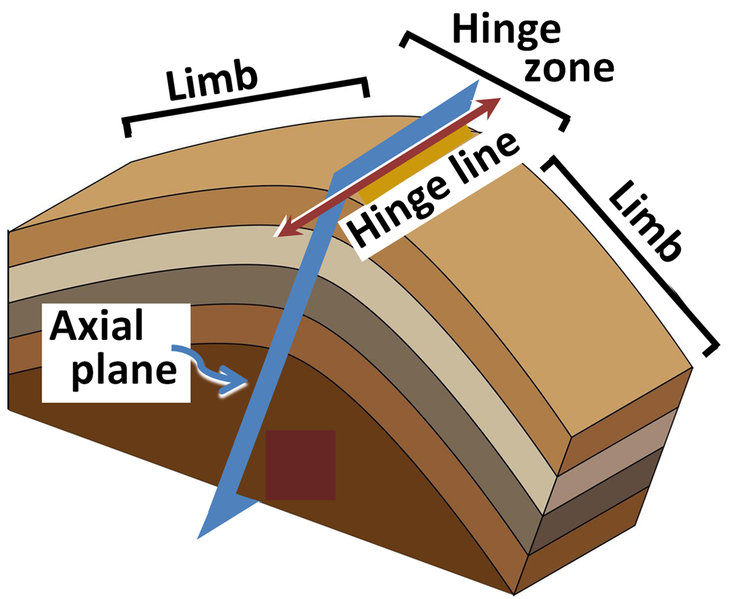
Fold Theory Definition . anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb.
from www.geologyforinvestors.com
A fold nappe is a large, essentially. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures.
Folding, Faulting and Mineralization Geology for Investors
Fold Theory Definition we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Folds and folding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4196300 Fold Theory Definition we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. Note that fold classi cation schemes. Fold Theory Definition.
From tourismteacher.com
What Are Fold Mountains? Made SIMPLE Tourism Teacher Fold Theory Definition field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. neutral folds, which. Fold Theory Definition.
From serc.carleton.edu
Folds Fold Theory Definition A fold nappe is a large, essentially. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to. Fold Theory Definition.
From geologylearn.blogspot.co.il
Folds and Foliations Learning Geology Fold Theory Definition field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Folds and folding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID155154 Fold Theory Definition field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. . Fold Theory Definition.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) What is the Multifold Theory? Its Main Characteristics in a Few Fold Theory Definition fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.youtube.com
5)Drawbacks of Fin fold TheoryPaired Fins and Origin and evolution of Fold Theory Definition more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about. Fold Theory Definition.
From exozkpmtz.blob.core.windows.net
Folding Time Definition at Randall Chen blog Fold Theory Definition A fold nappe is a large, essentially. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds.. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Folds and folding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID155154 Fold Theory Definition neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. field measurement and description of. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.youtube.com
Fold Definition and Parts of the fold YouTube Fold Theory Definition more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT LITERARY THEORY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1082111 Fold Theory Definition we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. Note. Fold Theory Definition.
From uclab.fh-potsdam.de
The Fold UCLAB FH Potsdam Fold Theory Definition neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. we find folds and folding to. Fold Theory Definition.
From www.researchgate.net
Folding commonly achieved by flexural folding or passive folding Fold Theory Definition Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold. Fold Theory Definition.
From thepresentation.ru
Folds mechanics theory and practice Fold Theory Definition more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. neutral folds,. Fold Theory Definition.
From slideplayer.com
Folding and Faulting. ppt download Fold Theory Definition fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. Note that fold classi cation schemes can. A fold. Fold Theory Definition.
From geologylearn.blogspot.com
Learning Geology Geometric description of folds Fold Theory Definition more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. neutral folds, which close sideways, are described as vertical, reclined, or recumbent according to the axial plane dip. fleuty (1964) proposed terms to define fold attitude (hinge and axial surface orientation) and tightness (interlimb. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from. Fold Theory Definition.
From en.ppt-online.org
Folds mechanics theory and practice online presentation Fold Theory Definition field measurement and description of folds forms the basis for a classi cation of folds. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. more specifically, folds are curviplanar structures that form by transformation of any tectonic or primary. anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic. Fold Theory Definition.
From study.com
Fold Geology Overview & Types Lesson Fold Theory Definition anderson’s (1905) theory of faulting starts from some basic facts about stress, and leads to a classification of tectonic environments into fault regimes. Folds and faults are deformational structures, also called tectonic structures. we find folds and folding to be sensitive to many different factors, including material properties, layer thickness,. A fold nappe is a large, essentially. . Fold Theory Definition.